In 2025, the global trade landscape was once again thrown into turmoil as the United States initiated a fresh wave of tariff hikes on several major trading partners, including Mexico, Canada, and China. This escalation of protectionist policies has sent shockwaves across international markets, reviving fears of a prolonged trade war and economic instability. The rationale behind these tariffs, their impact on global trade, and the future outlook for other exporting nations form the core of this analysis.
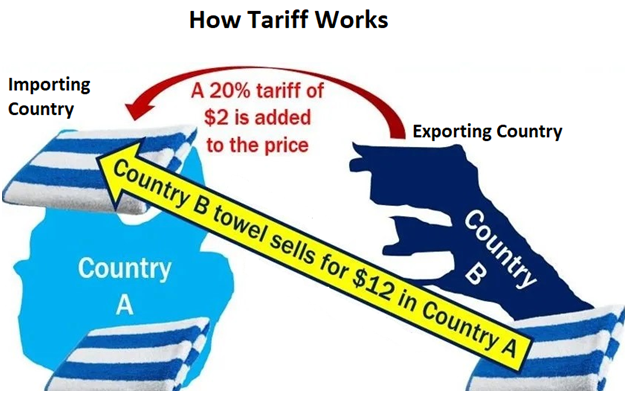
Major Reasons of Tariffs imposed by the USA
The renewed tariff war in 2025 can be traced back to multiple economic and political factors. The U.S. administration, citing concerns over:
- Trade imbalances, increasing trade deficit of USA
- Intellectual property theft, and
- domestic job protection,
- Counter perceived unfair trade practices.
- Protectionist measures to safeguard local industries from foreign competition.
- Illegal immigrants and drug trafficking across border between Canada –USA and Mexico-USA.
- political tensions with neighboring countries like Mexico and Canada
- Re-negotiate the USMCA or NAFTA
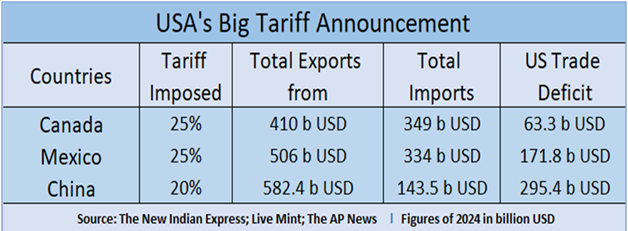
U.S. Tariff Rates: Then and Now
Before the latest round of tariff hikes, the average U.S. import tariff stood at approximately 3.4%, a relatively moderate rate by global standards. However, the 2025 tariff increases have significantly altered this landscape:
Prices in the USA markets will increase
Americans will experience inflation (of about 0.8% to 25%) in various sectors, especially on essential goods like:
- Medicines and Healthcare:
- Many pharmaceuticals and medical devices are imported from Canada and Mexico. Tariffs increase costs, making medicines and healthcare services more expensive.
- Groceries and Food Products:
- Mexico is a major supplier of fruits, vegetables, and meat to the U.S. Tariffs on agricultural imports will lead to higher grocery prices, particularly for fresh produce.
- Apparel and Consumer Goods:
- Clothing, footwear, and electronics imported from Mexico and Canada will see price hikes, impacting middle- and lower-income consumers the most.
- Automobiles and Electronics:
- Higher tariffs on Mexican and Canadian auto parts will make vehicles more expensive for American buyers. Similarly, electronic items like refrigerators, air conditioners, and TVs will see price increases.
- Construction and Housing Costs:
- Canada is a leading supplier of lumber to the U.S. Tariffs on lumber and steel will make housing and infrastructure projects costlier, raising home prices and rent.
More tariffs are likely to be imposed on:
In the upcoming months, the United States is poised to implement new tariffs targeting several countries and industries. The weighted average tariff of USA from 2.5% has increased to 10.5%. And this shall further increase as USA is planning to implement tariffs on:
- European Union (EU)
- Russia
- India and BRICS Nations
- Japan
- Colombia
- Industry-Specific Tariffs
- Automobiles, Semiconductors, and Pharmaceuticals: Starting April 2, 2025, the U.S. plans to impose 25% tariffs on imports in these sectors. This move aims to encourage domestic production and address trade imbalances.
These developments indicate a strategic shift in U.S. trade policy, focusing on protecting domestic industries and addressing trade deficits. Businesses engaged in international trade should monitor these changes closely to navigate the evolving landscape effectively.
Watch: https://youtube.com/live/xKnK0o-OfMc
